8-Step Guide to Using Instagram Ads [2023 Edition]
Instagram adds are posts that promote a business's products or services. The posts can appear in multiple ways, such as an Instagram feed, stories, or both. They can include images or video along with copy and a link to the web page of the company's choice.
Learn how to create successful Instagram ads by addressing an audience that's ready to shop on the platform.
Table of Contents :
- Introduction
- Advantages of advertising on Instagram
- How much do Instagram ads cost?
- Types of Instagram ads
- How to advertise on Instagram: setting up an ad step-by-step
- 6 Instagram ad tips
- Instagram ad examples
- Conclusion
- FAQ
1. Introduction:
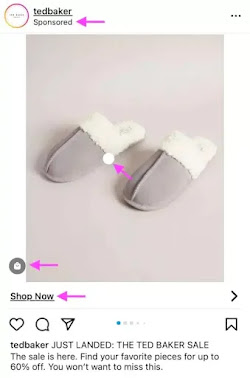
Instagram ads are posts businesses can pay to serve to specific target groups on Instagram. These ads appear in users’ feeds, Stories, and explore pages in the same format as organic content from other Instagram accounts. Instagram ads look similar to normal posts but always contain a Sponsored label to indicate that they are an ad. They also often have more features than a normal post, such as links, CTA buttons, and product tags.
2. Advantages of advertising on Instagram :
Learning how to make Instagram ads has a lot of potential benefits. Here are some of the advantages of using Instagram advertisements:
- Increase your brand’s following : Running Instagram ads can help boost your brand’s following by making your business easier to discover. When people share your posts or your posts go viral, you can reach a very large audience.
- Easily communicate with followers : Because people tend to check their social media accounts often, Instagram can be a good way to communicate with your followers. You can use different types of Instagram ads to let people know about new products, new services, or any significant changes you’re making to your brand.
- Inexpensive advertising option : While learning how to run Instagram ads has a bit of a learning curve, these ads are relatively cheap. Advertising on Instagram can be a good way to get more bang for your buck when it comes to marketing.
- Smart targeting : You can use smart targeting to target specific groups of customers. Smart targeting can be effective if you have a specific target audience who may be interested in a product or service .
3. How much do Instagram ads cost :
The cost of Instagram ads depends on the total budget, duration, and objectives you’ve set for your ad or campaign. You can set a daily or lifetime budget for your Instagram ads, so it’s up to you how much you want to spend. Note that there is no best practice for how much to spend, but Meta recommends starting with at least $5.00 per day.
4. Types of Instagram ads :
There are many different types of advertising formats on Instagram, including:
- Image ads
- Story ads
- Video ads
- Carousel ads
- Collection ads
- Explore ads
- Shopping ads
- Reels ads
5. How to advertise on Instagram:
There are two routes for creating Instagram ads campaigns: boosting an existing post and creating a new ad in the Meta Ads Manager . Promoting an existing post only takes a few taps and can be done right from the Instagram app, but lacks the customization options available in Instagram Ads Manager.
Below, we’ll walk you through most wanted method.
Using Instagram Boost
The easiest way to start advertising on Instagram is to promote one of your existing posts. This is similar to Facebook's boosts post option . If you have a post that is performing well in terms of engagement, promoting it within the app is a quick and easy method to scale up the post’s success—and show it to new people who aren’t following you yet.
You’ll need a business or creator account on Instagram to do this. You’ll also need to have a Facebook Business Page connected to your Instagram account (here’s how to connect your Facebook and Instagram account in Facebook Business Manager).
Then, it’s as simple as clicking Boost post on the post you wish to turn into an ad.
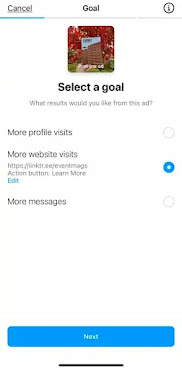
Next, choose your goal. You’ll have three options: more profile visits, more website visits, or more messages (this includes more WhatsApp messages).
Then, define your audience. You can either choose to let Instagram automatically determine your audience (based on your follower data). Or, you can create your own audience by manually entering your targeting options.
Now choose your daily budget and the duration of time you want the ad to run. You can either choose a set number of days or let it run infinitely until you manually pause it.
6. 6 Instagram ad tips :
Now you have everything you need to know about setting up and launching Instagram ads. The next step is designing effective visual assets for your ads.
Here are some tips for how to design attention-grabbing creative for Instagram ads:
1. Design mobile-first ads
More than 4.08 billion users access social media via a mobile device, so it's vital to design your creative for mobile viewing, not desktop.
Here are a few tips for designing mobile-first ads:
• When capturing video content, make sure to film in vertical (9×16) as this is easier to crop to 4×5 than from landscape
• Minimize the amount of text in your ads
• If you do add text, choose large font sizes that are easy to read on mobile screens
• Add animations and motion graphics to videos to quickly engage viewers
• Keep videos short (15 seconds or less)
2. Keep branding and messaging upfront
The first few seconds of your ad will determine whether a viewer will stop scrolling and watch The whole thing. That's why it's important to start your ad with the key message and showcase your branding within the first 3 seconds.
3. Use sound to delight
Data suggests that 69% of users consume social media with sound off. As such, it's important to design your ads for sound-off consumption and to use sound to delight users who do have sound on. Here's how to do that:
• Use visual elements to tell your story and deliver your key message without sound
- Add captions for any voiceover or scripted audio







.webp)







.webp)